Reconstruction module#
The circtools reconstruct module is based on FUCHS (FUll circular RNA CHaracterization from RNA-Seq), a Python program designed to fully characterize circular RNAs. It uses a list of circular RNAs and reads spanning the back-splice junction as well as BAM files containing the mappings of all reads (alternatively of all chimeric reads).
The reads from each circle are extracted by the reconstruction module and saved in an individual BAM files. Based on these BAM files, circtools will detect alternative splicing within the same circle boundaries, summarize different circular isoforms from the same host-gene, and generate coverage plots for each circRNA. It will also cluster circles based on their coverage profile. These results can be used to identify potential false positive circRNAs.
The reconstruction module depends on bedtools (>= 2.27.0), samtools (>= 1.3.1), Python (>= 3.7; pysam> pybedtools, numpy, and pathos), and R(>= 4.0.0; amap, Hmisc, gplots). All Python an R dependencies will be installed automatically when installing circtools. Please make sure to have the correct versions of bedtools and samtools in your $PATH.
General usage#
In order to characterize circRNAs from RNA-seq data the following steps are necessary:
Mapping of RNA-seq data from quality checked FASTQ files with STAR (BWA, TopHat-Fusion in preparation)
Detection circRNAs using circtools detect (CIRI, CIRCfinder or CIRCexplorer in preparation)
Run circtools reconstruct
Mapping of RNA-Seq data and detection of circRNAs#
Please see the documentation of circtools detect for instructions how to pre-process the data.
Usage of circtools reconstruct#
We continue by using the Jakobi et al. 2016 data set that also has been used as an example for the circtools detect module.
# download the wrapper scrips for the reconstruct module
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dieterich-lab/bioinfo-scripts/master/slurm_circtools_reconstruct.sh
# add execute permission
chmod 755 slurm_circtools_reconstruct.sh
# create output directory
mkdir 03_reconstruct
# download exon annotations required by the reconstruct module
wget https://links.jakobilab.org/mm10.ensembl.exons.bed.bz2
bunzip mm10.ensembl.exons.bed.bz2
# circtools reconstruct is independently run on all samples:
parallel -j1 slurm_circtools_reconstruct.sh {} 03_reconstruct/ mm10.ensembl.exons.bed 01_detect/ ::: ALL_1654_M ALL_1654_N ALL_1654_O ALL_1654_P ALL_1654_Q ALL_1654_R ALL_1654_S ALL_1654_T
Manually running the reconstruction module#
The above wrapper scripts handles all preprocessing and conversion steps. However, advanced users may want to start the module directly. circtools reconstruct starts the pipeline which will extract reads, check mate status, detect alternative splicing events, classify different isoforms, coverage profiles, and cluster circRNAs based on coverage profiles. Below a sample call for the reconstruct module in single sample mode using circtools detect input data:
# using STAR/circtools detect Input
$ circtools reconstruct -r 2 -q 2 -p ensembl -e 2 -T ~/tmp
-D CircRNACount
-J sample/Chimeric.out.junction
-F sample.1/Chimeric.out.junction
-R sample.2/Chimeric.out.junction.fixed
-B merged_sample.sorted.bam
-A [annotation].bed
-N sample
# if BWA/CIRI was used, use -C to specify the circIDS list (omit -D, -J, -F and -R)
# For details on the parameters please refer to the help page:
$ circtools reconstruct --help
Optional reconstruct module#
The additional module denovo_circle_structure_parallel can be employed to obtain a more refined circle reconstruction based on intron signals. The circRNA-separated bamfiles (step 2) are the only input required for the module. If an annotation file is supplied, unsupported exons will be reported with a score of 0, if no annotation file is supplied, unsupported exons will not be reported.
$ denovo_circle_structure_parallel -c 18 -A [annotatation].bed -I output/folder -N sample
# output/folder corresponds to the output directory of the circtools reconstruct pipeline
# sample corresponds to your sample name, just as specified for the pipeline
Required input data#
circRNA IDs#
CircRNA data data can be provided via a generic table with the structure found below:
circID |
read1,read2,read3 |
|---|---|
1:3740233|3746181 |
MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:2107:10994:20458,MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:1116:13529:8356 |
1:8495063|8614686 |
MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:2118:9328:9926 |
The first column contains the circleRNA ID formated as folllowed chr:start|end. The second column is a comma separated list of read names spanning the back-splice junction.
BAM input files#
Alignment files produced by any suitable read mapping tool. The files have to contain all chimerically mapped reads and may also contain linearly mapped reads.
BED annotation file#
A BED file in BED6 format. The name should contain a gene name or gene ID and the exon_number. You can specify how the name should be processed using -p (platform), -s (character used to separate name and exon number) and -e (exon_index).
Chr |
Start |
End |
Name |
Score |
Strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
67092175 |
67093604 |
NR_075077_exon_0_0_chr1_67092176_r |
0 |
- |
1 |
67096251 |
67096321 |
NR_075077_exon_1_0_chr1_67096252_r |
0 |
- |
1 |
67103237 |
67103382 |
NR_075077_exon_2_0_chr1_67103238_r |
0 |
- |
Output produced by circtools reconstruct#
*.alternative_splicing.txt#
This file summarizes the relationship of different circRNAs derived from the same host-gene. A sample file structure given below:
Transcript |
circles |
same_start |
same_end |
overlapping |
within |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
NM_016287 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
. |
. |
. |
. |
NM_005095 |
1:35358925-35361789,1:35381259-35389082,1:35381259-35390098 |
1:35381259-35389082|1:35381259-35390098, |
. |
. |
. |
NM_001291940 |
1:236803428-236838599,1:236806144-236816543 |
. |
. |
. |
1:236803428-236838599|1:236806144-236816543, |
Description of the data columns:
Transcript: Transcript name as defined by the bed-annotation file
circles: Comma-separated list of circRNA ids derived from this transcript
same_start: Comma-separated list of circRNA pairs separated by
|. Pairs in this column share the same start coordinates. A “.” indicates that there are no circle pairs that share the same start coordinates.same_end: Same as same_start, only now, circle pairs share the same end coordinates.
overlapping: Comma-separated list of circRNA pairs separated by
|. Pairs in this column share neither start nor end coordinates, but their relation is such that: start.x < start.y && end.x < end.y && start.y < end.xwithin: Same as overlapping, but circRNA pairs have the following relation: start.x < start.y && end.x > end.y
*.exon_counts.bed#
These files are BED formatted and describe the exon-structure. The files can be loaded into any genome browser. Each line corresponds to a circRNA.
Chr |
Circle Start |
Circle End |
Transcript |
Num of Reads |
Strand |
Start |
End |
Color |
Num of Exon |
Exon Lengths |
Relative Exon Starts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
chr1 |
35358925 |
35361789 |
NM_005095 |
9 |
+ |
35358925 |
35361789 |
0,255,0 |
3 |
521,61,170 |
0,2269,2694 |
chr1 |
20749723 |
20773610 |
NM_016287 |
4 |
- |
20749723 |
20773610 |
0,255,0 |
4 |
159,90,143,159 |
0,7443,21207,23728 |
Description of the data columns:
Chr: Chromosome of circRNA
Circle Start: The 5’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 1-index based
Cirlce End: The 3’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 0-index based
Transcript: Transcript name as defined by the bed-annotation file
Num of Reads : Number of reads supporting this chimeric junction, in other words, reads that are chimerically mapped to this junction
Strand: Strand of the host-gene
Start: Copied Circle Start to stay conform with BED12 format
End: Copied Circle End to stay conform with BED12 format
Color: pre defined color the exons will show up in the genome viewer (0,255,0 -> green)
Num of Exon: Number of exons in this circRNA consists of
Exon Lengths: Comma-separated list of the length of each exon
Relative Exon Starts: Comma-separated list of the relative starting positions of the exons within the circle boundaries.
*.exon_counts.txt#
This file contains similar information as the previous file, just more detailed information on the exons. Each line corresponds to one exon.
sample |
circle_id |
transcript_id |
other_ids |
exon_id |
chr |
start |
end |
strand |
exon_length |
unique_reads |
fragments |
number+ |
number- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
hek293 |
1:35358925-35361789 |
NM_005095 |
NM_005095 |
2 |
1 |
35358924 |
35359446 |
+ |
522 |
9 |
9 |
4 |
5 |
hek293 |
1:35358925-35361789 |
NM_005095 |
NM_005095 |
3 |
1 |
35361193 |
35361255 |
+ |
62 |
3 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
hek293 |
1:35358925-35361789 |
NM_005095 |
NM_005095 |
4 |
1 |
35361618 |
35361789 |
+ |
171 |
9 |
9 |
4 |
5 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
3 |
1 |
20749722 |
20749882 |
- |
160 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
0 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
4 |
1 |
20757165 |
20757256 |
- |
91 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
7 |
1 |
20770929 |
20771073 |
- |
144 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
hek293 |
1:20749723-20773610 |
NM_016287 |
NM_016287 |
8 |
1 |
20773450 |
20773610 |
- |
160 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
0 |
Description of the data columns:
sample: Sample name as specified by the user. This is useful if the user wants to merge files from different samples
circle_id: circRNA-ID. The circleID is formatted to be copy and pasted to a genome browser for easy access
transcript_id: Transcript name as defined by the bed-annotation file. This is the best fitting transcript. i.e. the splicing variants that contains the most exons that are actually covered
other_ids: Alternative Transcript names that are either just as fitting, or contain more or less exons as supported by reads
exon_id: Exon number relative to the host-gene of the circularized exon. One circle may have more than one exon. These will be listed as consecutive lines
chr: Chromosome the circRNA is located on
start: 5’ start of the exon, relative to the reference strand, 0-based
end: 3’ end of the exon, relative to the reference start, 0-based
strand: Strand of the host-gene
exon_length: Length of the current exon
unique_reads: Number of unique reads associated with the chimeric junction. When the data is paired end, then both ends are considered as separate reads.
fragments: Number of broken fragments aligning to the circle
number+: Number of reads spanning the chimeric junction on the forward strand
number-: Number of reads spanning the chimeric junction on the reverse strand (if reads are only from one strand, this may indicate that there is a sequencing bias)
*.mate_status.txt#
This output file contains the results of analyzing the amount of how often each fragment spans a chimeric junction. A fragment can either span the chimeric junction once (single), only one end spans the junction, twice (double) both ends span the chimeric junction, or more than twice (undefined).
circle_id |
transcript_ids |
num_reads |
min_length |
max_length |
single |
double |
undefined |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1_20749723_20773610 |
NM_016287 |
4 |
790 |
790 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
1_35358925_35361789 |
NM_005095 |
9 |
754 |
754 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
Description of the data columns:
circle_id: The circRNA ID in the form chr_start_stop
transcript_ids: Names of the corresponding annotated transcript IDs
num_reads: Total number of reads for this circRNA
min_length Minimal length of exons intersecting the circRNA
max_length: Maximal length of exons intersecting the circRNA (if only one exon same as min_length)
single: Number of single break points for this circRNA
double: Number of double break points for this circRNA
undefined: Number of undefined break points for this circRNA
*.skipped_exons.bed#
Chr |
Circle-Start |
Circle-End |
Transcript |
Ratio |
Strand |
Intron-Start |
Intron-End |
Color |
NumExon |
IntronLength |
RelativeStart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
chr5 |
178885614 |
178931326 |
NM_030613 |
60.0 |
. |
178913072 |
178931236 |
255,0,0 |
3 |
1,146,1 |
0,30950,45711 |
chr6 |
161034259 |
161049979 |
NM_001291958 |
40.0 |
. |
161049332 |
161049852 |
255,0,0 |
3 |
1,520,1 |
0,15073,15719 |
Description of the data columns:
Chr: Chromosome of circRNA
Circle-Start: The 5’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 1-index based
Cirlce-End: The 3’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 0-index based
Transcript: Transcript name as defined by the BED annotation file
Ratio: Ratio of reads of this skipped exon
Strand: Strand of the host-gene
Intron-Start: The 5’ site of intron. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 1-index based
Intron-End: The 3’ site of the intron. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 0-index based
Color: pre defined color the exons will show up in the genome viewer (0,255,0 -> green)
Num of Exon: Number of exons in this circRNA consists of
IntronLengths: Comma-separated list of the length of each intron
RelativeStart: Comma-separated list of the relative starting positions of the introns within the circle boundaries.
*.skipped_exons.txt#
circle_id |
transcript_id |
skipped_exon |
intron |
read_names |
splice_reads |
exon_reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5_178885614_178931326 |
NM_030613 |
5:178916564-178916710 |
set([('5', 178913072, 178931236)]) |
MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:2103:10044:24618,MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:2115:19571:6931,MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:1119:25537:8644 |
3 |
5 |
6_161034259_161049979 |
NM_001291958 |
6:161049332-161049852 |
set([('6', 161049332, 161049852)]) |
MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:1113:25288:9067,MISEQ:136:000000000-ACBC6:1:2116:11815:3530 |
2 |
5 |
Description of the data columns:
Chr: Chromosome of circRNA
Transcript_id: Transcript name as defined by the BED annotation file
Skipped_exon: Coordinates of the skipped exon
Intron: Set of introns
read_names: Unique read names identifying this skipped exon
splice_reads: Number of reads supporting the splice site
exon_reads: Number of reads supporting the exon
*.sample_name.exon_chain_6.bed#
Chr |
Exon-Start |
Exon-End |
ID |
Ratio |
Strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11 |
33286413 |
33286525 |
11:33286413-33287511|0|0 |
5 |
. |
11 |
33287338 |
33287511 |
11:33286413-33287511|1|0 |
9 |
. |
Description of the data columns:
Chr: Chromosome of circRNA
Exon-Start: The 5’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 1-index based
Exon-End: The 3’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 0-index based
Name: CircRNA ID, number of exon, coverage
Ratio: Coverage ratio
Strand: Strand not reported, always “.”
*.sample_name.exon_chain_12.bed#
Chr |
Circle-Start |
Circle-End |
ID |
#reads |
Strand |
Circle-Start |
Circle-End |
Color |
#Exons |
Exon lengths |
Exon starts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11 |
33286413 |
33287511 |
11:33286413-33287511|0|0.446265938069 |
7 |
. |
33286413 |
33287511 |
255,0,0 |
2 |
112,173 |
0,925 |
10 |
68959806 |
68960249 |
10:68959806-68960249|0|0.984198645598 |
5 |
. |
68959806 |
68960249 |
255,0,0 |
2 |
146,290 |
0,153 |
Description of the data columns:
Chr: Chromosome of circRNA
Circle-Start: The 5’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 1-index based
Cirlce-End: The 3’ site of the chimeric junction. This is relative to the reference strand, i.e. start < end! The location is 0-index based
ID: CircRNA ID, running number, coverage
#reads: Number of reads covering the circRNA
Strand: Strand (always “.”)
Circle-Start: See above
Circle-End: See above
Color: pre defined color the exons will show up in the genome viewer (0,255,0 -> green)
Num of Exon: Number of exons in this circRNA consists of
Exon lengths: Comma-separated list of the length of each exon
Exon Starts: Comma-separated list of the relative starting positions of the exon within the circle boundaries.
sample [folder]#
1_35358925_35361789_9reads.sorted.bam
1_35358925_35361789_9reads.sorted.bam.bai
1_20749723_20773610_4reads.sorted.bam
1_20749723_20773610_4reads.sorted.bam.bai
*.coverage_pictures/ [folder]#
Using R, circtools will generate a graphical representation of each circle’s coverage profile, preserving the exon information as coloured segments. The smoothed profiles are saved as PNGs in a separate folder for easy examination by eye.
Sample circRNA coverage plot#

*.coverage_profiles/ [folder]#
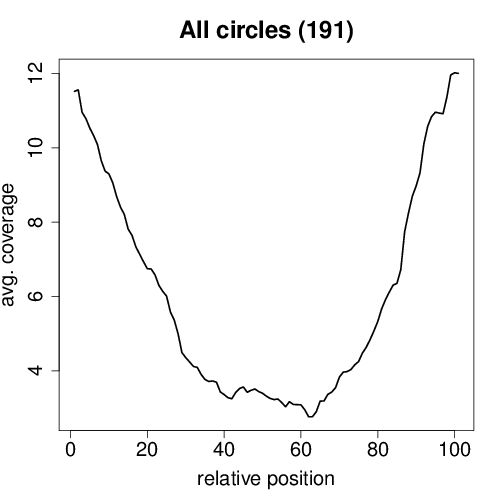
Circtools will accumulate all coverage profiles, normalize the profiles by circle length and cluster the circles based on their coverage profiles. The clustering is performed on all circles. Additionally, to avoid that the clustering will only group the circles based on their length, a group-wise clustering is performed. Here the circles are separated based on their length into small (<500 BP), medium (500–1,000 BP), and long (≥1,000 BP) circles. Based on correlation a K-means clustering is performed using the R package amap.
All circles#
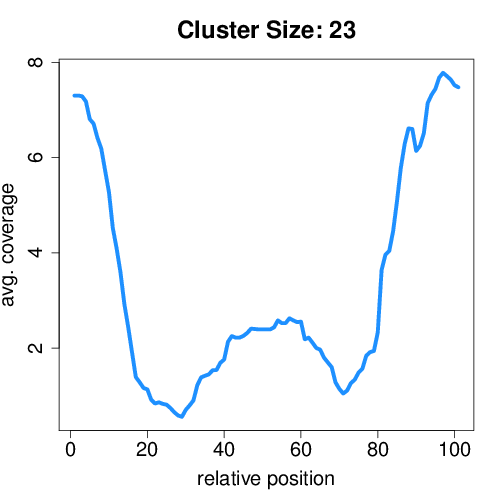
Short circles#
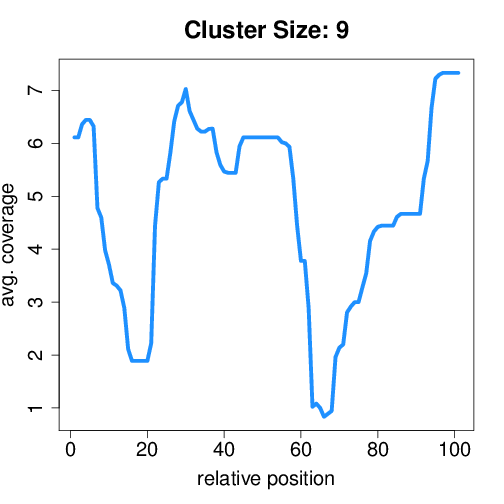
Medium circles#
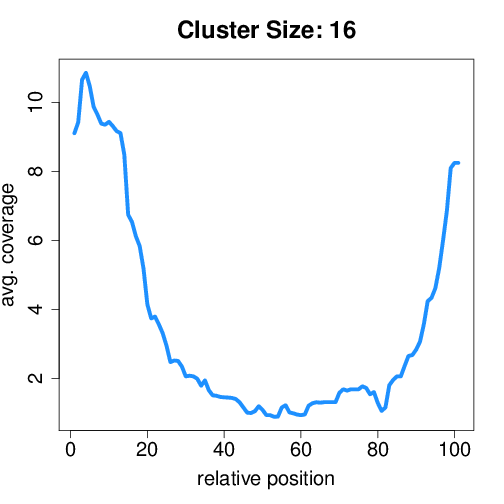
Long circles#
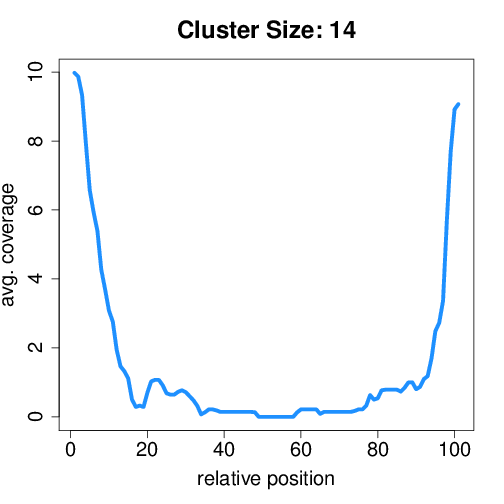
Profiles of all circles#